Arteriovenous malformation and anastomoses
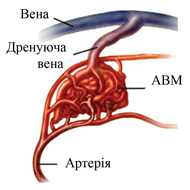
Arteriovenous malformation is a plexus of abnormally widened arteries and veins with the absence of a capillary network. AVM is characterized by an acceleration of blood flow through the arteries and veins. AVM – congenital pathology. The most serious complication is hemorrhage (intracerebral haemorrhage) with a high risk of disability of patients, development of severe neurological deficit or death, regardless of the type of malformation.
Arteriovenous malformations occur in 0.14% – 2% of the population.
The ratio of AVM to sacral aneurysms is 1: 5,3.
The average age of patients with diagnosed AVM is ≈ 33 years.
64% of AVM is diagnosed before the age of 40.
- Advantages of endovascular methods:
– Few invasiveness;
– Low traumatism;
– The size of the malformation does not matter;
– Conducting surgical interventions under local anesthesia (carrying out functional tests);
– The effect immediately after the intervention.
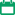
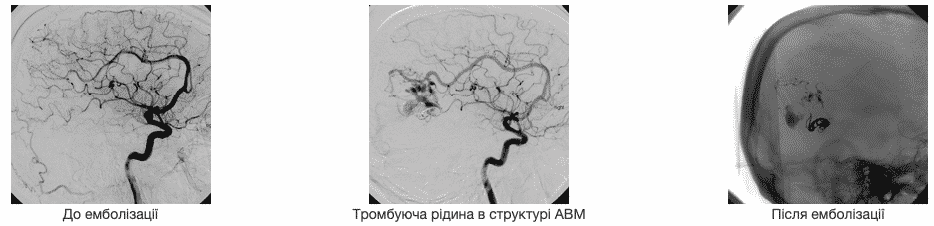
The goal of endovascular embolization – the maximum possible exclusion of AVM from the blood flow, is achieved by the introduction of an embolisate directly into the arteriovenous shunts in the cavernous part (naidus) of the malformation.
• Transarterial access is effective in the presence of direct AV shunts, with a small number of afferent arteries
• Combined arterial-venous access (S. Gudak) – the most radical, technically complex. Effective with all AVM.
History of the use of means for embolizing AVM
• 1904 – hot wax
• 1965 – pieces of muscle
• 1972 – the dura mater
• 1974 – separable cylinders
• 1976 – silk
• 1977 – PVA
• 1978 – polymerizing substances:
– histoacryl
– glue
1991 – polymeric substance “Embolin”
• 1991 – microcoils, hydrocoils …
• 1999 – Onyx
Endovascular embolization
Description of the method.
The goal of endovascular embolization – the maximum possible shutdown of AVM from the blood flow, is achieved as a result of obliteration of arteriovenous shunts in the cavernous part (naidus) of malformation. Liquid embolizing substances are used:
- Histoacryl (B.Braun, Germany) or Onyx (EV-3, USA)
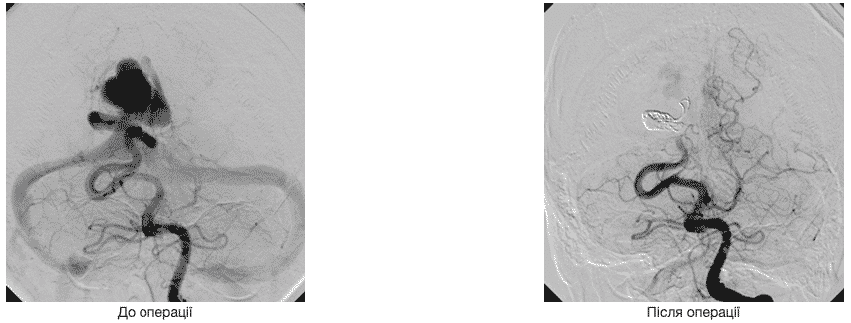
Examples of switching off arteriovenous malformations from the bloodstream
AVM side projection
AVM direct projection
AVM direct projection
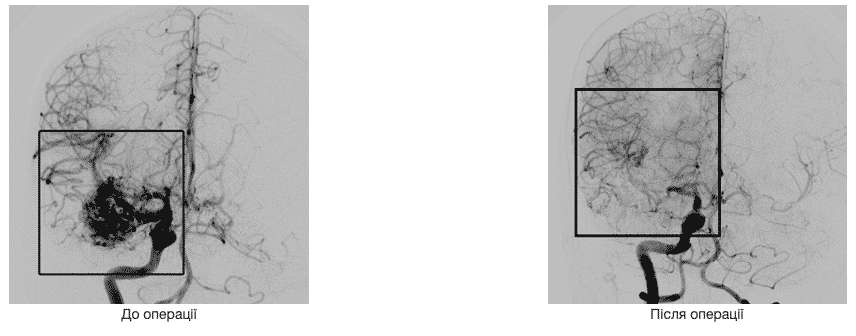
Spiral computed tomography is a three-dimensional image of an embolizing substance in the structure of malformation
ARTERIOVENOUS MALFORMATIONS OF THE SPINAL CORD
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
- 85% – progressive neurological deficit
-
10-20 % – sudden myelopathy, usually in patients under the age of 30, caused by hemorrhage
METHODS OF OCCLUSION
- NBCA (N-butyl-2-cyanoacrylate)
- Embospheres (Guerbet Co., France)
- Pulsar (MIS Co., the USA)
- Microballoons (Balt Co., France) Microcoils PVA with silk threads
- Embolizing composition “Embolin”
- ONYX
- histoacryl (B.Braun, Germany)
Arteriovenous anastomoses
Modern endovascular methods of treatment of arteriovenous anastomoses:
- Using spirals or balloons
- With the help of liquid embolizing substances

Arteriovenous fistula is an abnormal connection between the artery and the vein. Native pathology is often combined with the presence of several communication vessels. In this regard, the complete elimination of pathology is often impossible. Treatment can consist in embolizing the area of pathology by the method of stationary occlusion or in its surgical removal.
Examples of treatment of arteriovenous anastomoses:
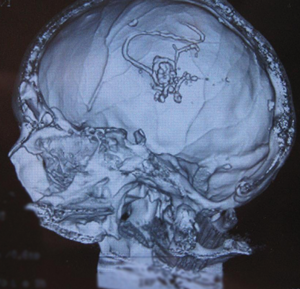
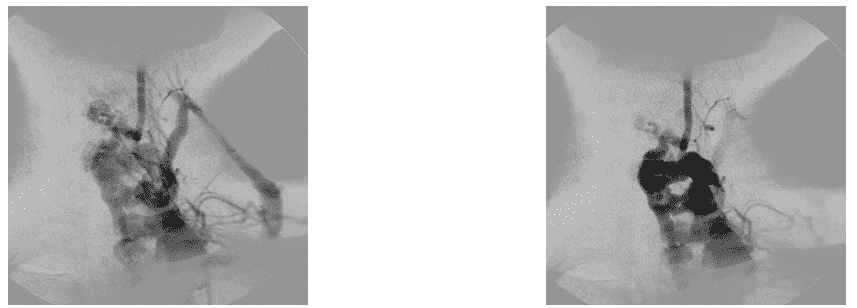
AV shunt of anterior cerebral artery
The operation was performed by the method of stationary balloon occlusion of the place of formation of pathological shunting
Angiogram of AVM mixed type of spinal cord
Before exclusion from the circulation
After the operation, the AVM is turned off from the circulation
Arteriovenous anastomoses mixed type
CT scan before surgery
The AV shunt of the posterior cerebral artery is disconnected using separable GDC spirals
From the pool of the internal carotid artery AVM is disconnected from the blood stream using a liquid embolizing agent